Have you ever wondered how long different animals live in captivity? Then you need to read this article on animal lifespans. On the infographic below you can check out some of the most popular animals in zoos, including some of the domestic ones.
Get this as a poster for your clinic or classroom! Order HERE!
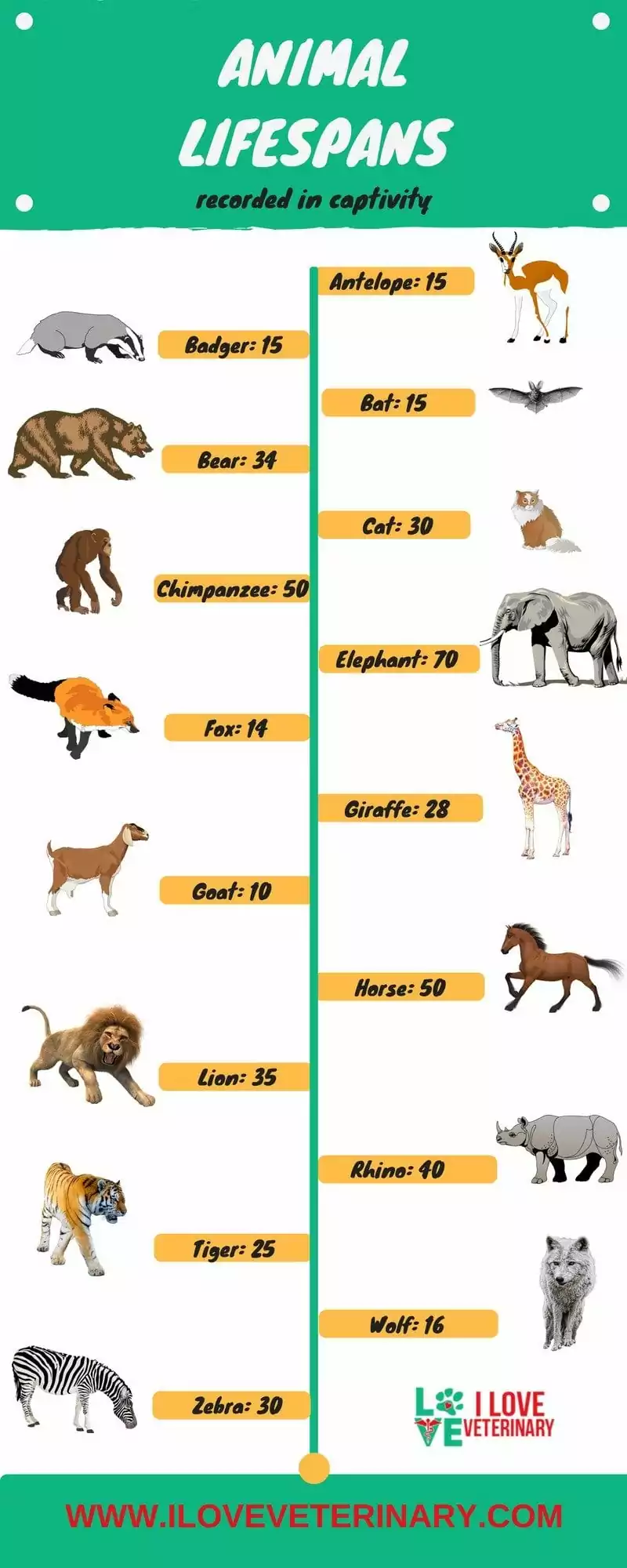
The Lifespans of Animals in Captivity
Because of the changing nature of science, the exact lifespans of different animals are not well-known or constant. Some generalities can be made about certain types of animals, however.
Animals that spend most of their time in water tend to live longer than similar land-dwelling creatures. For example, there are fish living in at least one lake that has no apparent limit on its age. One particular fish was aged 500 years old. This theory is also supported by whales and other cetaceans whose life spans have been attributed to their environment.
Some studies show that smaller animals tend to live longer than larger ones due to certain biological such as metabolism rate and heartbeats. Although animal lifespans can range drastically, there are certain trends that should be noted.
The Relationship Between Lifespan and Animal Size
A generalization about animal lifespans is the relationship between the animal’s size and how long it lives. Smaller animals tend to live longer than larger animals because smaller animals have fewer cells (meaning more rejuvenation), faster metabolisms (making cellular damage occur at a faster rate), and lower heartbeats; all of which make them age faster.
For example, elephants only live for an average of 50 years while mice normally only live for four or five years. However, this theory is not universal as shown by one animal living much longer than its expected lifespan. The animal in question was believed to be 500 years old; whereas the average age for a fish of its species is only around 80 years.
Another animal lifespan generalization is that animals living in water tend to live longer than similar land-dwelling creatures. For example, there are fish living in at least one lake that has no apparent limit on its age. This theory can also be seen with whales and other cetaceans whose life span has been attributed to their environment.
Other animals such as tortoises and alligators have made it past the century mark and may even reach 200 years old.
Other Factors That Influence Animals’ Lifespans
There are many factors that influence animal lifespan, among these factors are the animal’s size, habitat, and lifestyle. Generally, animals follow a pattern of exponential growth in their early years followed by a slowing of their rate of growth. For example, dogs have an average lifespan between 10-12 years though some dogs can live up to 20 years while others only see six months.
The larger the animal is, the larger its body mass therefore it would take longer for cells within the animal to replicate before dying off or being replaced. For this reason, large animals tend to live much longer than smaller animals.
Living in an urban environment tends to mean that your animal will be much safer from predators when compared to an animal living in the wild which means they are likely to live longer. In the wild animals are not only more susceptible to predators but also have competition from other animal species for food and shelter which leads them to a life of stress and anxiety.
These factors all play a role in animal lifespan, especially when comparing animal lifespans of wild and domesticated animal species.
There is no denying that having access to vet care dramatically increases animal lifespan, whether it’s because you live in an urban environment or because you’ve taken your dog on daily walks to meet its exercise requirements; both factors can increase animal lifespan.
For this reason, animal caretakers who provide regular exercise and annual checkups with their veterinarian tend to see their pet live longer than those whose animal simply roams around outside without these basic necessities.
