Veterinary ECG machines can be confusing at first for new grad veterinary nurses when they start working at a veterinary practice. It takes time and practice to get used to its practicalities, modalities and knowing when and how to react. There is no doubt that ECG is an important monitoring tool during and after surgery in a veterinary clinic.

What is an ECG machine?
ECG (electrocardiogram) in veterinary medicine is a recorder of the electrical activity of the heart at rest.
It provides an accurate assessment of the heart rate, and it registers the type of disturbance in the heart (rhythm).
The veterinary ECG machine does not record the cardiac and mechanical output.
Uses of the veterinary ECG:
- To monitor the depth of anesthesia, pain, and stress
- To observe post-surgical patients
- To monitor an animal with a chronic condition
- It is useful when arrhythmia is suspected
 Placing the electrodes:
Placing the electrodes:
It is important to apply electrode gel to the skin of the animal before using the veterinary ECG and read the manual previously. These colors apply to Uk machines.
- Red- right foreleg, behind the elbow
- Yellow- left foreleg, behind the elbow
- Green- left hindleg, front of the stifle
- Black lead- right hindleg front of the stifle
Recommendations during veterinary ECG monitoring
If possible, carry out the ECG recording in a quiet and stress-free environment to avoid a decrease in the recording quality.
The patient should be in right lateral recumbency, but this may vary for cats and animals with dyspnoeic (unable to breathe or to breathe with difficulty).
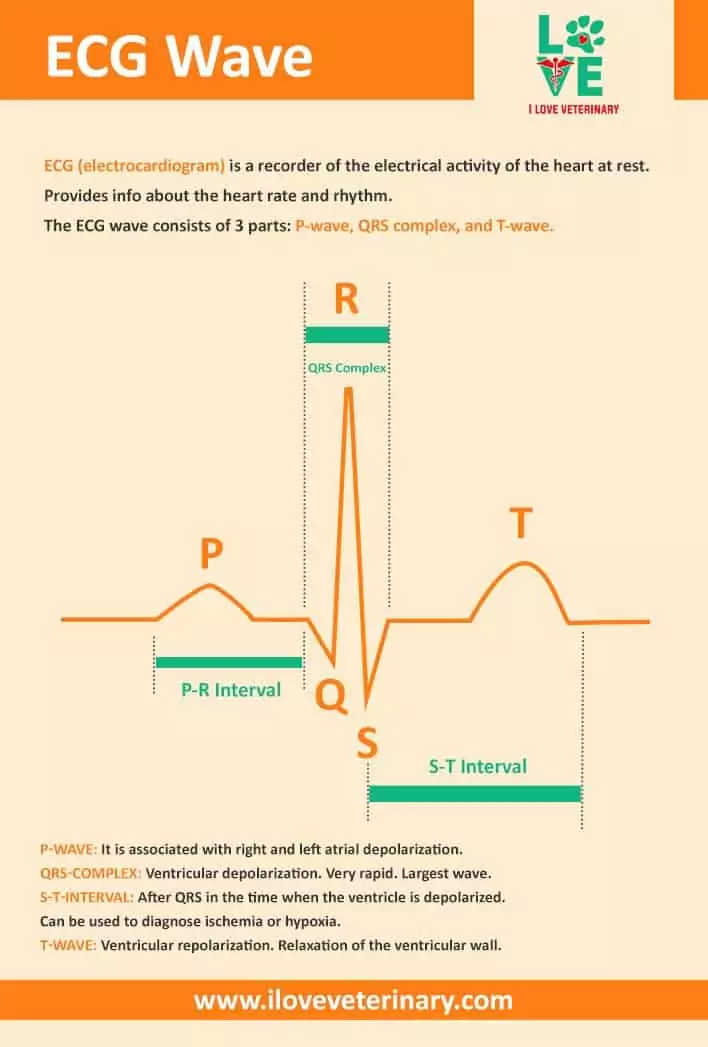
Parts of an ECG wave
The ECG wave consists of 3 parts: P-wave, QRS complex, and T-wave.
- P-wave: it is associated with right and left atrial depolarization.
- QRS-complex: ventricular depolarization. Very rapid. Largest wave.
- S-T-interval: after QRS in the time when the ventricle is depolarized. It can be used to diagnose ischemia or hypoxia.
- T-wave: ventricular repolarization. Relaxation of the ventricular wall.
Veterinary ECG interpretation
To make it more visual for our readers, we decided to embed a video to this article from the veterinary technician David Liss.
If you found this veterinary ECG article useful, make sure to check out our infographic on animal heart rates.

 Placing the electrodes:
Placing the electrodes: