What Isotonic Fluids?
Isotonic fluids are two solutions that have the same osmotic pressure across a semipermeable membrane. Because of this, free movement is allowed across the membrane. It doesn’t interfere with the concentration of solutes on each side.
Isotonic fluids are used for intravenous nutrition by administering a solution of minerals, sugar, and water. They are commonly used in hospitals to help maintain electrolyte balance or in patients with impaired kidney function in order to decrease the risk of dehydration in the case that they cannot drink.
The use of isotonic fluids has been shown to help maintain fluid volume and electrolyte balance.
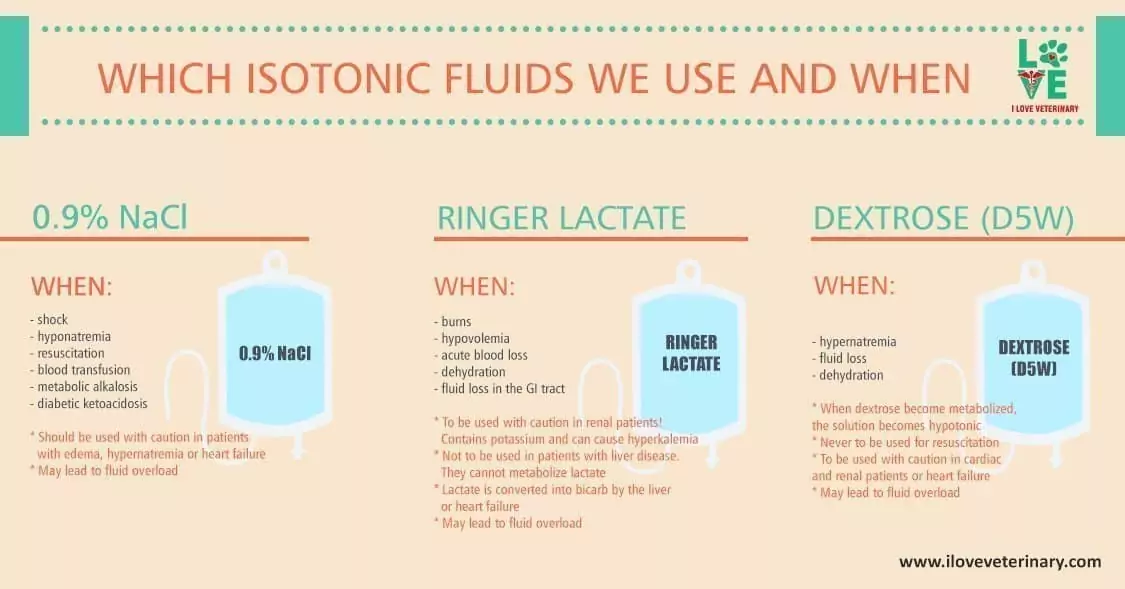
List of Isotonic Fluids Used in Veterinary Medicine
NaCl 0.9%
NaCI Isotonic Veterinary Medicine is an all-natural supplement for horses that combines electrolytes, extra prebiotics, and trace minerals in one easy-to-administer formula.
It helps horses overcome leg weakness or dysfunction caused by nerve damage or fatigue. We have products for both performance and medical care. These are products to help your horse feel their best so they can do what they do best…work!
Many people have heard of isotonic solutions and know that they contain two parts: water and a salt mixture. The human body can retain up to 85% of the salt mixture, so any animal given an infusion will still be able to maintain water balance.
One type of solution used in animals is NaCI Isotonic Solution, also called “Vitamin C” by its makers. This solution has been used to treat a wide range of ailments in animals, from footrot in cattle to scours in calves. It is also used as a tonic for hens to boost the quality of their eggs and as an aid for mothers that have lost their litter.
This solution is easy to make and it is great to have handy around the barn or pasture because it can be used for many different purposes. Animals can even be given oral doses of the solution, although it is often given subcutaneously or intravenously.
Used to treat:
- Shock
- Hyponatremia
- Resuscitation
- Blood transfusion
- Metabolic alkalosis
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
Special care instructions:
- Should be used with caution in patients with edema, hypernatremia, or heart failure.
- May lead to fluid overload.
Ringer Lactate
Ringer lactate is a solution with the same salt concentration as blood. A balanced electrolyte solution, Ringer lactate has all of the ingredients needed for cell function in the right concentrations. The lactate in Ringer lactate is derived from lactic acid, which is produced when muscles are metabolizing glucose without oxygen – i.e., during exercise.
A number of factors go into choosing an intravenous therapy fluid, but one of the most important criteria is matching pH to the body’s acidity level.
Used to treat:
- Burns
- Hypovolemia
- Acute blood loss
- Dehydration
- Fluid loss in the GI tract
Special care instructions:
- To be used with caution in renal patients! Contains potassium and can cause hyperkalemia.
- Not to be used in patients with liver disease. They cannot metabolize lactate.
- Lactate is converted into bicarb by the liver or heart failure.
- May lead to fluid overload.
Dextrose (D5W)

Dextrose is a specific type of sugar that is also known as glucose or grape sugar. It is formed by the digestion of starch. Dextrose can be consumed in the form of drinks, foods, or powders without impacting blood sugar levels because it doesn’t raise blood glucose levels quickly.
The main use for dextrose is to prevent hypoglycemia after prolonged gluconeogenesis, which usually happens when an animal has not eaten for more than 12-24 hours and its body produces excess glucose from liver glycogen stores.
Used to treat:
- Hypernatremia
- Fluid loss
- Dehydration
Special care instructions:
- When dextrose becomes metabolized, the solution becomes hypotonic.
- Never to be used for resuscitation.
- To be used with caution in cardiac and renal patients or heart failure.
- May lead to fluid overload.
