What is Spay and Neuter and What Does it Mean?
Have you ever wondered what the spay and neuter difference is? The clinical term for “spay” is Ovariohysterectomy. It is a procedure by which the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus are removed from a female dog or cat.
The result of this procedure is for the animal to be unable to reproduce, it stops the breeding instinct-related behavior and eliminates the heat cycle.
The clinical term for “neuter” is Orchiectomy. It is a procedure by which the testes are removed from a male dog or cat. The procedure stops the ability for the male to reproduce and it also reduces/eliminates the breeding behaviors.
Get this Spay and Neuter Poster for your clinic or classroom!
Top Reasons to Spay and Neuter Your Pet
- Reduce spraying and marking – This means that if your pet had the habit to pee in order to mark his territory (in your home), there is a high probability that this behavior will be eliminated and in worst cases, it will be reduced.
- Reduce roaming – Do you know that the most common reason for lost pets is because roaming for mating? Yes, our beloved pets are looking to reproduce and unfortunately they escape from the yard, home or even from our leash.
- Reduce aggression – There are numerous cases that have shown reduced aggression in spayed or neutered pets. If aggression is a big problem for your pet, you should consider this as an option to resolve the situation.
- Lower risk of cancers – One of the most common cancers in dogs are testicle cancer, mammary glands cancer and other cancers connected to the reproductive system. If you spay or neuter your pet, you can lower the risk.
- Decrease overpopulation – Maybe the most important reason on this list. Spaying and neutering makes a big difference: Just one unaltered female dog and her offspring can produce 67,000 puppies in only six years. In seven years, one female cat and her offspring can produce an incredible 370,000 kittens! Source: PETA
- Increase life span – Spaying helps prevent uterine infections and breast tumors in females and prevents testicular cancer and some prostate problems. Source: ASPCA
Key Differences Between Spaying and Neutering
Spaying
Spaying a female dog or cat refers to the process where her ovaries and uterus are removed. This is done through an incision on the animal’s abdomen and uterus/ovaries lifted out for removal.
Spaying is usually accompanied by a hysterectomy (removal of the uterine horns and body) and can also include ovariectomy procedures, known as “Ovariohysterectomy”.
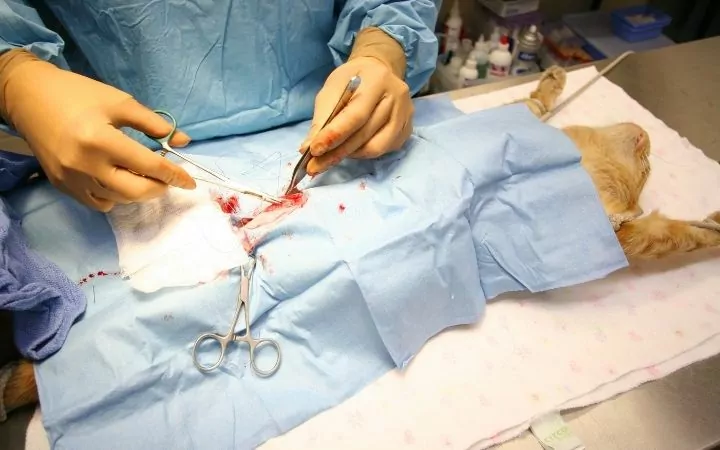
A spayed female will no longer go through heat cycles, she will not get pregnant, and will no longer have the risk of uterine or ovarian cancer.
Spaying a female dog or cat is one of the most common surgical procedures performed on pets in North America with spay/neuter being routine for almost all pet dogs and cats in some areas, especially when they are very young. In order to spay a female animal, she must be at least four months old, however, kittens as young as eight weeks can be spayed if they weigh more than two pounds.
Neutering
Neutering a male dog or cat refers to the process where his testes are removed through an incision near the scrotum. A neutered male will no longer be able to impregnate a female. A spayed female’s season (heat) is also referred to as being “in heat”.
Neutering reduces the risk of testicular cancer, might reduce some unwanted behaviors associated with mating instincts, and allows for easier pet travel in most countries.
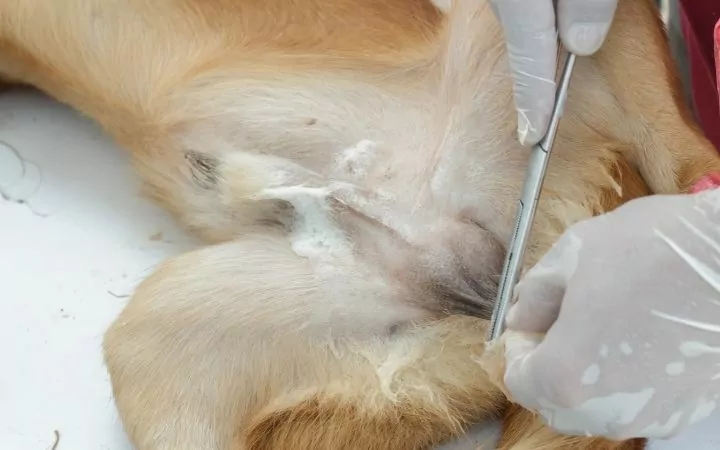
Neutered males are more likely to live longer lives since they are not at risk of testosterone-triggered diseases such as prostate cancer later in life.